EOS is a blockchain platform for working with decentralized applications (DApps). It provides users with a set of tools that greatly facilitate the creation of such software products. The goal of the project is to create a system that will have the advantages of already existing blockchains (Bitcoin, Ethereum, etc.). The resulting product should be easy to use, meet the high demands of speed and scalability.
EOS was developed by Block One company, managed by Daniel Larimer, who is also the founder of such high-profile projects as BitShares and Steemit.
The slow projected emission of new tokens (up to 5% per year) will be distributed among the community members through smart contracts selected for this purposes, which will finance the operation and development of the network.
The distribution of EOS token began on June 26, 2017 at 13:00 UTC. It will be carried out completely on Ethereum blockchain during 341 days. Over the entire period, 1 billion (1’000’000’000) tokens in ERC-20 format will be distributed:
- During the first 5 days, two hundred million (200’000’000) or 20% of EOS tokens were distributed.
- An additional seven hundred million (700’000’000) EOS tokens are distributed in parts of two million (2’000’000) over 350 consecutive 23-hour periods.
- Finally, one hundred million (100’000’000) or 10% of EOS tokens to be distributed will be reserved for block.one as a developer of EOS.IO and will not be sold or transferred in Ethereum network during the entire distribution period.
The distribution of EOS tokens is similar to an auction, where the price for all is the same and the maximum that everyone wants and can pay in a given period of time. By the end of the 5-day interval and by the end of each 23-hour interval described above, the corresponding specific amount of EOS tokens mentioned above will be distributed proportionally among all authorized buyers in accordance with the total number of ETH tokens contributed during the corresponding time period.
The minimum contribution for any period of EOS tokens distribution is 0.01 ETH.
EOS tokens distribution scheme is based on the following principles:
- No one should get anything for nothing.
- Everyone should get a certain market price.
- Everyone should have equal opportunities to participate.
- The presence of incentives for developers.
- Purchasing more than 50% of distributed tokens should be economically disadvantaged.
- The cost of transaction should be as low as possible.
Block.one company that develops EOS, does not provide for the creation of a functioning platform, within which the EOS token will be used. If any public platform will be created to work with EOS token, it will be a product from other developers. Moreover, if you run your own platform on EOS, then you can make any changes to EOS.io software to optimize the performance of your product.
The agreement on the purchase of EOS states that EOS tokens do not give the rights, possibilities of use, do not have goals, attributes, functional possibilities or functions, express or implied; EOS tokens do not grant the right to participate in EOS platform, even if EOS platform is launched and the development of EOS.IO is completed, and EOS.IO software is accepted and implemented. Also: “Buyer acknowledges, understands and agrees that: (a) EOS tokens may have no value; (b) there is no guarantee or representation of liquidity for the EOS tokens; and (c) the block.one Parties are not and shall not be responsible for or liable for the market value of EOS tokens, the transferability and/or liquidity of EOS tokens and/or the availability of any market for EOS tokens through third parties or otherwise”.
Thus, this Agreement does not give an idea of what value EOS tokens carry to their owners even if the platform is successful. Journalists from Wall Street Journal in this regard called EOS a token "without meaning." However, the defenders of the project believe that the creators of the platform simply want in this way to provide their token with the maximum possible protection from regulators. And in the FAQ on the official EOS website, you can learn about the use of EOS tokens at the end of the ICO.
The end of the distribution period of tokens is scheduled for June 1, 2018 — this is when the coins will become fixed in Ethereum blockchain (will not be transferable), and until that time they can be transferred and moved to peer-to-peer platforms that are subject to third party management. After the end of ICO, the owners of the tokens will have 23 hours to register the public key of their Ethereum address for which the tokens were purchased. Confirmed possession in this way gives the following possibilities:
- Equal exchange for the tokens of those platforms that will be released on EOS base.
- Taking part in management: for the tokens of blockchain created on EOS to become transferable, there should be an approval from owners of 15% of the tokens.
Reddit has detailed instructions on how to register EOS tokens.
The following exchanges reported that they will take all the concerns of registration for their users:
EOS uses DPOS (Delegated Proof of Stake) algorithm.
According to the algorithm, owners of tokens of blockchain, which is adapted for EOS.IO can choose block producers in the course of unceasing voting, and anyone can decide to participate in the creation of blocks and get the right to create a number of blocks proportional to the number of votes regarding to all other block producers. If a block producer skips a block and does not create a single block within 24 hours, then he is excluded from the process until the special notification that such block producer must send to the blockchain to confirm his intention to continue his work. This ensures the smooth operation of the network and minimizes the number of skipped blocks by excluding unreliable block producers from the schedule.
During normal operation of the algorithm, no fork occurs in the chain, since the block producers work together, and do not compete with each other. If a fork does occur, the network switches to a longer chain. Each block producer must simultaneously create them on only one branch of a fork, but if he starts creating blocks on two branches at once, he will be excluded from the process.
Additional protection of the blockchain is the use of Transaction as a Proof of Stake (TaPoS) algorithm. EOS.IO software requires each transaction to include the hash of the last block header. This hash serves two purposes:
- Prevents the repeat of transaction on forks that do not include a block with this transaction.
- It signals the network that a particular user and his stake are on a specific fork.
Over time, all users directly confirm the block, which makes it difficult to fake chains, because a fake will not be able to transfer transactions from the legitimate chain.
EOS is consensus operating system on a blockchain that provides databases, account permissions, scheduling, authentication and communication for Internet applications using parallelism, providing blockchain with scalability to millions of users and millions of transactions per second.
EOS can support thousands of commercial-scale applications using parallel processing and asynchronous communication. It separates authentication from action. For example, a transfer is a simple action of reducing the balance of one account and increasing another, but all authentication steps check signatures, make sure that the account has enough money, etc. But the authentication steps are needed only once — when a block is created. After the block has become irreversible and was added to blockchain, you never need to do authentication again. EOS places the source code in the blockchain, so that the terms of the contract are readable by humans, everyone can see them, and developers can optimize and compile them on different machines, all without breaking consensus.
EOS is also flexible in terms of that you have to run only those applications that you need. If you are working on exchange, you do not need to run social media, and you can configure your local node to process only the data you need. Not every node needs to have and maintain the full state of blockchain. EOS also stores source code, not assembly one, and provides role based permissions.
EOS network as a whole is not vulnerable to DOS attacks. Possession of EOS tokens gives users a proportional share of network bandwidth, its memory and computing power. Thus, spammers can use only a part of the network, the one to which they are entitled, taking into account their EOS tokens.
DOS attacks can be possible in individual applications, depending on the architecture of these applications, but these attacks can never damage the entire network. Startups with a very small package invested in the network will have guaranteed, reliable bandwidth and computing power, even if many other malicious subjects try to spam several large network applications.
If the application breaks down or stops working, the selected block producers can freeze the application until the bug is fixed, and then update the code. So if a decentralized organization works on EOS, it, for example, can be frozen, corrected and updated, all without the need for hard forks or stopping other applications on this blockchain.
EOS tokens are neither securities nor any other financial instruments, they are not intended for investment or speculative purposes, and should not be considered as investments. In this connection, SEC rules on tokens did not apply to EOS. Debevoise & Plimpton LLP, New York, acts as a block.one external legal adviser on the current distribution of EOS tokens.
In addition, the US citizens, residents, and organizations were excluded from the purchase of EOS tokens during the distribution of tokens. This decision was made because of some logistical problems associated with differences in regulation in many states of the US, including, among other things, the legislative order of BitLicense in New York State.
In early September 2017, due to the changes in China regulatory base regarding the distribution of cryptographic tokens in general, block.one decided as a precaution measure to immediately exclude citizens and residents of China, as well as organizations formed in accordance with the laws of China (in the aggregate “Chinese subjects”), from the procedure for acquiring EOS tokens. Chinese entities are strictly prohibited from using EOS smart contract and/or buying EOS tokens. If a Chinese person uses an EOS smart contract and/or buys EOS tokens, that person has done so and made EOS token purchase agreement on an illegal, unauthorized and fraudulent basis, and such an agreement will be invalid.
- "Architecture and Logic" evaluation: 10 points out of 10. The outlook is positive.
Mechanisms and principles of emission — 3 points out of 3.
Blockchain (architecture and consensus building mechanism) — 4 points out of 4.
Licensing and legal aspects — 3 points out of 3.
The outlook is positive. Emission, distributed for such a long time, gives an opportunity to anyone who wants to take part in it. There is enough time to study the project, follow dynamics of its development and make a balanced decision. Consensus and architecture are stable and secure, tested on other blockchains: Bitshares, Steemit.
Graphene 2.0 blockchain underlying EOS platform has a speed of more than 3’000 TPS and it can be increased many times over. On tests, Graphene was able to get 10’682 transactions per second. In this case, creators talk about the possibility of increasing to 100’000 transactions per second.
The use of Graphene-networks technology allows to achieve significant improvements in terms of scaling by eliminating a number of properties of traditional blockchains.
EOS will use parallelization to scale the network, probably to millions of transactions per second. This will enable EOS to support thousands of DAPPs (decentralized applications) on a commercial scale.
EOS will use asynchronous communication and separate authentication from the execution process to get more speed. It also will not have transaction fees, and EOS does not require counting operations.
EOS philosophy is to provide applications with tokens and blockchain by giving them the opportunity to engage in their business processes.
EOS will include a set of web-based interface development tools, self-describing interfaces (data that goes to the blockchain can be read by humans, but also compressed), self-described database schemes and a declarative permission scheme. This allows to get exactly calibrated permissions management level, where you can easily delegate specific permissions to other accounts.
EOS will be the first operating system on the blockchain, providing much faster development of decentralized software applications and significantly reducing costs.
It will be possible to conduct ICO for one or several projects on EOS.
The platform implements the possibilities of decentralized trading on various services. This feature will be quite useful for both individual users and large companies that need to protect personal information. A variety of organizations can use EOS network without being afraid for the security of confidential data. In addition, the system allows to develop platforms of any size.
EOS benefits:
- high scalability parameters — the maximum capacity of infrastructure, designed for decentralized applications, allows to provide support for an incredibly large number of commercial applications with parallel execution of tasks, communication asynchrony and separation of transactions authentication from their execution;
- flexibility of work — the ability to freeze and correct problematic developments and use the web assembly;
- a wide range of options — the use of declarative resolution scheme, self-determination of database schemes, the possibility of self-description of interfaces and tools allows to fully work on the creation of a variety of products.
Accounts
EOS.IO allows to use unique, human-readable names from 2 to 32 characters as account identifier. The name is chosen by the creator of the account. To enable data storage, the account must be credited with a minimum amount at the time of creation. In addition, account names may contain a namespace index, while only the owner of the @domain account can create accounts like @ user.domain.
Each account has the ability to send structured messages to other accounts, and it can also define the procedures for processing incoming messages (scripts). EOS.IO allocates to each account a protected database, access to which is only available to its own message handlers. Message handlers can send messages to other accounts. The combination of messages and their automated handlers is a smart contract in EOS.IO.
Authentication
EOS offers developers the ability to use a ready user authentication system that stores private information on the client side. In this system, it is possible to divide into levels of privacy depending on the group to which the member being verified belongs. The functions of sharing the database and storing information on the user's local computer outside the blockchain will be implemented. The system of backup recovery account is constantly upgraded.
Cloud storages
Cloud storages and server hosting are provided by EOS. This means that developers can use existing infrastructure to develop and run applications without worrying about purchasing such equipment. After launching the application, programmers get the tools to conduct analytics and set the necessary restrictions.
The holder of tokens on a blockchain, running on EOS.IO software, which does not need to immediately use all or part of the available power, can lease or rent out unused bandwidth to other accounts.
Phase 1 — a minimally viable testing environment that includes an autonomous node, source contracts, a virtual machine API, an RPC interface, command line tools (eosc), and basic developer documentation, was completed in the autumn of 2017.
In September 2017, EOS.IO Dawn 1.0 release, which is the first pre-release of EOS.IO SDK (Software Development Kit), was launched. In addition to the software itself, this release includes documentation and instructions for developers on creating a private P2P network for testing smart contracts. Release Description:
https://github.com/EOSIO/eos/releases
EOS.IO Dawn 2.0, the next major pre-release, was launched at the end of 2017. EOS.IO Dawn 2.0 includes several important features not found in EOS.IO Dawn 1.0, including:
- Limiting the speed of resource use (prevention of spam/misuse).
- Generation of Merkle Tree (for communication between blockchains).
- Modernization of management.
- More reliable SDK.
- General infrastructure improvement.
- An example snapshot on ERC-20 tokens.
The goal of EOS.IO Dawn 2.0 is to be functional enough to be able to launch a viable blockchain on it.
Since December, the development team has been working on the merging of two development lines: Dawn 2.x and Dawn 3.0. Dawn 3.0 was in its early alpha stage by the end of the first quarter of 2018, and a preliminary release was held on April 6, 2018.
Additional new features in Dawn 3.0 Alpha Release include: pending transactions, betting pools, a new foreign exchange contract and a new token standard. A complete list of new features can be found in the official announcement of the release.
In addition to computing power, owners of tokens based on EOS.IO software will get access to free cloud storage, hosting and load bandwidth via IPFS/HTTPS; this access can be used without spending or transferring tokens. The storage solution on EOS.IO software can also provide public hosting to those who do not have tokens.
On June 2, 2018, the release of EOS.IO 1.0 platform was launched.
All available software is on Github
Those with development experience can start here.
Any user can launch a local node by following the instructions provided here: How to Build EOS.IO (eosd)
Documentation for interacting with the local node using RPC:
https://eosio.github.io/eos/group__eosiorpc.html
A quick guide to creating accounts, transferring funds, loading contracts and interacting with these contracts through eosc and eosd can be found here: eosc — command line client
Other documentation: Easy Docker Guide for EOS, Instructions for configuring Ubuntu to build EOS, Installation and launching EOS on Windows.
Full catalog: https://eosio.github.io/eos/modules.html
There are several examples of contracts that can be used as a starting point. For information on available APIs, see How to Write Contracts
The #eosdev tag is launched on Steemit, questions and/or answers regarding development are published under this tag. Sensible questions, answers and tutorials get upvote.
Developer support is also provided in Telegram chats:
- Chat for communication on the development of EOS (En): https://t.me/joinchat/EaEnSUPktgfoI-XPfMYtcQ
- Russian chat EOS Dev:
The source code development activity is 89% (according to the data from coingecko.com site on March 24, 2018).
The total number of updates in the last 4 weeks: 843.
EOS is the first operating system on the blockchain, it supports the operation of any DAPP (decentralized application), taking on a certain set of functions.
EOS.IO blockchain is designed to simplify cross-chain interactions. This is achieved by simplifying the creation of evidence of the existence of messages and the confirmation of the sequence of messages.
This evidence, combined with the application architecture developed for messaging, allows to hide the details of inter-block communication and validation from application developers. The platform uses Merkle's proof for Light Client Validation. The purpose of LCV is to create a relatively light proof of existence that can be confirmed by anyone who tracks a relatively light data set. In this case, the goal is to prove that a particular transaction has been included in a particular block and that the block is included in the verified history of a particular blockchain.
- "Functionality and software platform" evaluation: 10 points out of 10. The outlook is positive.
Performance and scalability — 2 points out of 2.
Built-in mechanisms and functions — 3 points out of 3.
Product — 4 points out of 4.
Integration options — 1 point out of 1.
The outlook is positive. High speed and scalability. There is an active development of the product in accordance with the planned dates. Convenient functionality with a wide range of features.
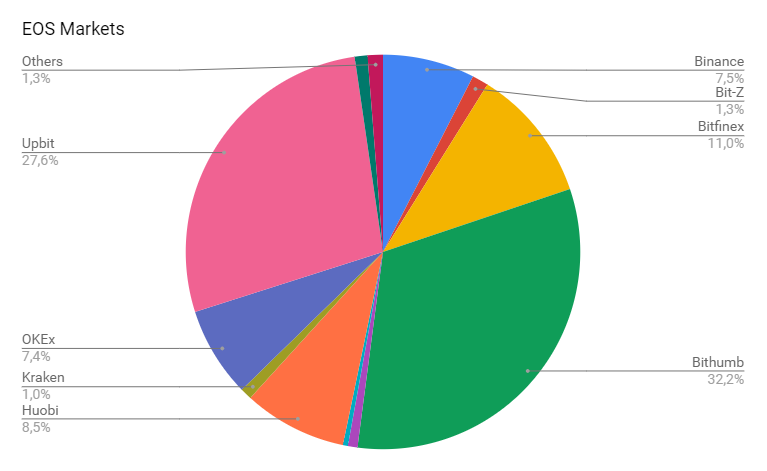
EOS can be purchased at the following trading platforms: Bitfinex, Binance, Hitbtc, Kraken, Liqui, Bit z, Mercatox, Livecoin, Yobit, Tidex, etc.
The main demand engine for this coin was the moment when the opportunity to buy it on these resources appeared. Most of these platforms are popular all over the world.
Distribution of trading on exchanges (according to coinmarketcap.com website as of March 24, 2018):
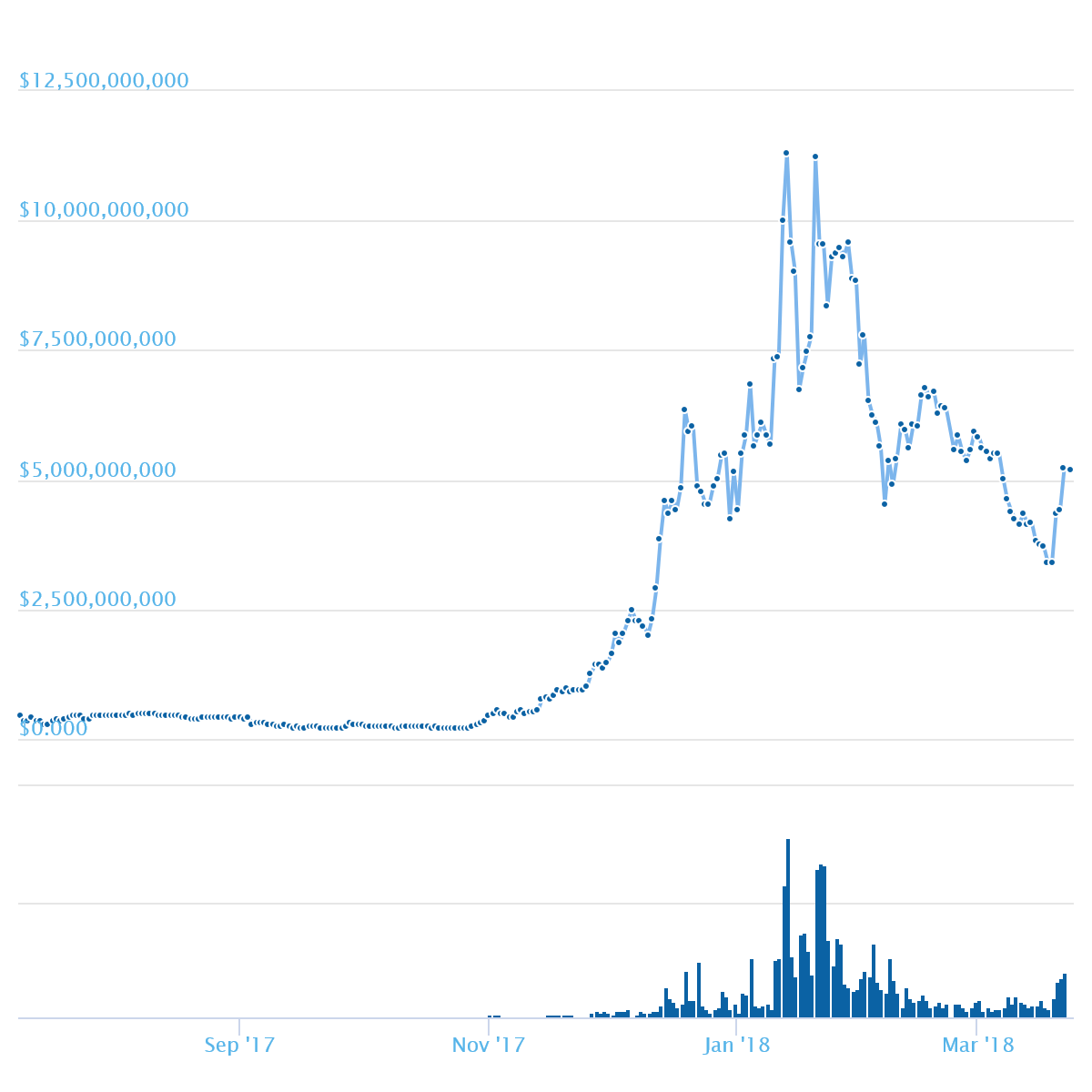
Despite the fact that not much time has passed since cryptocurrency appeared, EOS has already entered the TOP-10 of all world cryptocurrencies in terms of capitalization. In early July, EOS was in 9th place, in November it dropped to the 13th, and now it is on the 6th (as of March 24, 2018). The maximum value of capitalization was reached on January 13, 2018 and amounted to more than $11 billion. The size of capitalization currently stands at $5’174’505’336 (according to data from coinmarketcap.com as of March 24, 2018).
Capitalization dynamics:
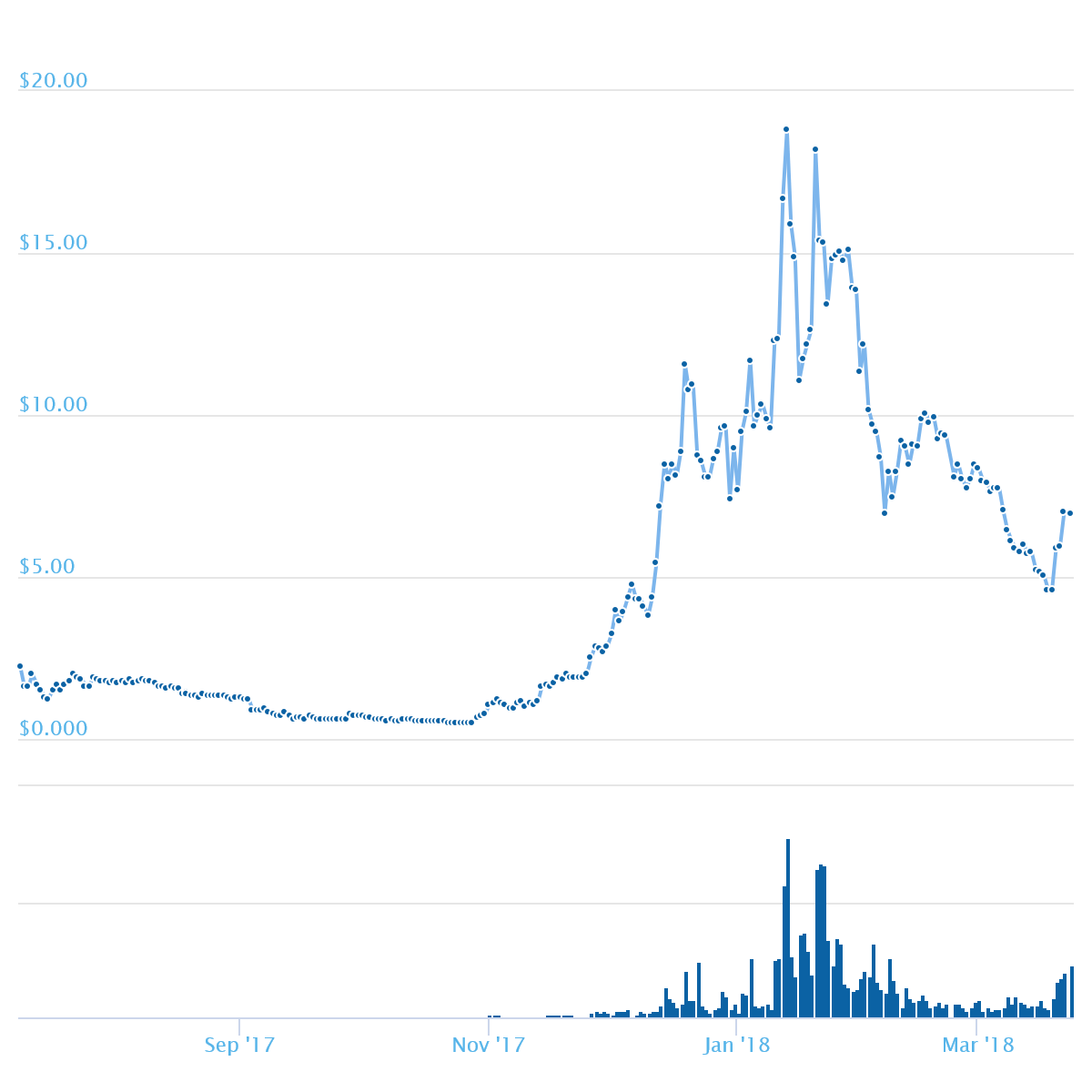
A noticeable token growth began on June 28, 2017, when the cost of one coin was only $0.01. And on July 1, the price reached $0.9. After a short period of stabilization, the rate went up sharply and reached the level of $5.09 by the end of July 3. Then there was a long period of stabilization until November 2017, when the token price ranged between $0.5 and $2.5. Then a gradual increase began. And throughout the winter of 2017-2018, there was very strong volatility. The maximum price of the token at this point was reached on January 13, 2018 and amounted to $18.79. Now the price of one token is $6.94 (according to coinmarketcap.com website as of March 24, 2018).
Token price dynamics:
- "Statistics" evaluation: 8 points out of 10. The outlook is neutral.
Distribution — 3 points out of 3.
Capitalization dynamics — 3 points out of 4 (susceptibility to market influence)
Token price dynamics — 2 points out of 3 (high volatility for the last 3 months, susceptibility to market influence)
The outlook is neutral. A very famous project, which is traded on a large number of exchanges. However, the rate shows high volatility lately. The increase in token price is possible in the 2nd quarter of 2018 in connection with the release of next version of the product.
Road Map was published 9 months ago, the link to it is currently non-working:
https://github.com/EOSIO/Documentation/blob/master/Roadmap.md.
In fact, at the moment this document is officially absent. Perhaps this is due to the mention of the project team representative in the official blog that the development team is reviewing the stages of project development.
However, you can see the translation into Russian of the original version of Road Map.
The deadlines are scheduled to phase 4 “Parallel Optimization” (winter/autumn 2018). The final phase “Formation of clusters” immediately follows the previous one and is not defined in time.
According to Road Map, single-threaded implementation will be completed by June 2018, after which the work on multithreading will begin. In early November, the developers reported that the work on the parallel execution engine started 8 months earlier than the schedule, and they believe that it will be completed by June 2018. The list of works on the implementation of the engine includes a complete rewrite of chainbase — the database underlying Steem technology.
You can follow the news on Steemit:
Technical WhitePaper:
- https://github.com/EOSIO/Documentation/blob/master/TechnicalWhitePaper.md — in English
- Translation into Russian:
https://github.com/EOSIO/Documentation/blob/master/ru-RU/TechnicalWhitePaper.md
WhitePaper of EOS.IO Storage:
https://github.com/EOSIO/Documentation/raw/master/EOS.IO%20Storage.pdf
The technical White Paper describes in detail the principle of consensus building algorithm, accounts management and their protection, the principles of EOS.IO software, the project economics. The information is written in a completely accessible language, understandable not only to developers.
- "Analysis of Road Map and White Paper" evaluation: 6 points out of 10. The outlook is neutral.
White Paper — 5 points out of 5.
Road Map — 1 point out of 5 (1 point for the release of the first version of Road Map).
The outlook is neutral. High quality of White Paper is leveled by the actual absence of the actual Road Map version. It is necessary to monitor the release of a new version of Road Map. In the case of appearance of a document of good quality, the outlook can be changed.
Team
EOS team is led by veterans of blockchain:
- Brendan Blumer, CEO since 2014. Blumer was engaged in cryptocurrency mining in MMORPG in the US and he is the founder of the groups "Okay.com" in Hong Kong and "1Group" in India.
- Dan Larimer — project Technical Director, participated in the creation of BitShares crypto exchange and the first social network on blockchain — STEEM. STEEM and BitShares turned out to be the most used blockchains in terms of the number of transactions created by actual users. It is Larimer who is the inventor of the widely accepted concepts of “Proof of Stake” and “Decentralized Autonomous Corporations”, which many people attribute to Vitalik Buterin.
- Brock Pierce, block.one partner, venture capitalist, pioneer of the digital currency market in games, raised over $200 million for his companies. Brock is the chairman of Bitcoin Foundation and one of the founders of Blockchain Capital.
- Ian Grigg, partner of block.one, financial cryptographer who has been building cryptographic platforms for more than 20 years. Grigg is the inventor of Ricardian Contract and the co-author of Triple Record Accounting.
There is no detailed information about all the project participants, but all of them are employees of Block.one company. The organization is exempt by Cayman Islands association. The main activity of the project is aimed at software building — EOS team employs specialists who collaborate with consultants from different parts of the world, which allows to effectively focus on business-class problems and develop effective solutions with integration of blockchain technologies into the system.
One of the reasons for the popularity of EOS is the presence of Dan Larimer in the team. Many criticize the ambiguity of his platforms and the fact that he often leaves them at beta testing stage. So, after launching BitShares, Dan left the project immediately after the difficulties appeared with the attachment of electronic money to the asset market. A few days later he launched a new project — Steemit. The platform resembled Reddit social network and made it possible to generate income based on the popularity of user records. Some met the service with enthusiasm, others criticized it, blaming it in instability and forcing artificial deficiency.
Dan himself, answering questions about these projects, says that even though they had certain difficulties, they became the necessary basis for creating EOS. Each of the platforms contributed to the solution of the problem that hinders the widespread commercial use of blockchain. So BitShares proposed the principle of horizontal scalability, contributing to a multiple increase in the speed of transactions. Steemit also helped to solve the problem of growing commissions, giving new methods of interaction between users without any transaction costs.
Considering the reputation of Dan Larimer, his new project was expected to provoke mixed reactions. Some members of crypto community say that they will believe all the statements only after seeing some developments, others blame the creator of EOS platform in ordinary fraud.
Investors
On January 16, 2018, Block.one announced that, together with Tomorrow Blockchain Opportunities (TomorrowBC — a venture company specializing in innovations that use blockchain technology), will create a fund for exclusive investment in the potential of using EOS.IO software with initial seed investments of $50 million. This is the first announcement of the launch of Block.one EOS VC affiliate program, designed to stimulate the development of innovations based on EOS.IO.
On January 23, 2018, Block.one and Galaxy Digital LP (Galaxy Digital), functioning as a commercial fund for digital assets, announced the creation and financing of a joint venture. It will focus on the development of EOS.IO ecosystem and on strategic investment of projects that use blockchain EOS.IO software. Under the agreement, $325 million will be invested to create a new EOS.IO Ecosystem Fund (EOS.IO Ecosystem Fund). Fund’s assets will be used for investment and maintenance of new projects.
On March 21, 2018, Block.one and FinLab AG (one of the first and largest investors focused on FinTech sector in Europe) announced the signing of an agreement of intent to form and capitalize a new fund with the value of $100 million. The fund will be managed by FinLab, its goal is to make strategic investments throughout Europe using projects with EOS.IO open source software.
Block.one plans to raise about $1 billion in partnership with leading venture capital investors to stimulate EOS.IO software development.
Partners
The project is actively supported by many world known partners. Among them:
- Bitfinex;
- FenBushi Capital;
- Hyperchain Capital;
- Blockchain Capital.
Bitfinex representatives announced that they want to use Bitfinex experience and EOS.IO technology to provide fast, transparent and secure digital asset exchange, creating a decentralized exchange based on EOS — EOSfinex.
- "Analysis of the project team and affiliated persons" evaluation: 10 points out of 10. The outlook is positive.
The number of the team — 2 points out of 2.
Team structure — 3 points out of 3.
Team competencies — 3 points out of 3.
Affiliated persons — 2 points out of 2.
The outlook is positive. Numerous and experienced team led by crypto legend Daniel Larimer, the team has extensive experience in the field of blockchain technologies. The investment program launched in January has already raised $475 million and plans to raise about $1 billion in total to stimulate the development of EOS.IO software. The team is attracting new partnerships, including the partnerships from large exchanges.
EOS competitors: Ethereum, Tezos, NEO, Quantum, Cardano.
Tezos is a very promising development. However, due to disagreements among its founders, the prospects for Tezos are still very hazy. In the worst case, with the further growth of the conflict, there is some risk of general closure of the project and the return of all funds, collected during the ICO, back to investors. Tezos would have already been launched a few months ago, if not for all the ongoing trials. Recently, Kathleen Breitman has promised that the project will start soon. Tezos will allow tokens holders to influence the operation and development of the project. It will feature smart contracts, an algorithm for Delegated Proof of Stake and a model with two blockchains. The control system resembles Dash, while Michelson is an own language of smart contracts, that will allow to hold official verification so that developers can confirm that their code is mathematically correct.
Cardano can be a serious competitor if it launches successfully and keeps all its promises. When the platform launches, its blockchain will support decentralized applications, its own management model and will be aimed at achieving a balance between confidentiality and regulation. According to the plans of developers, Cardano, running on its own Ouroboros Proof of Stake algorithm, should be a fast and scalable blockchain. Though, Daniel Larimer criticized this algorithm, suggesting that Charles Hoskinson has stolen his idea, but DPoS algorithm still remains the best.
NEO has problems with decentralization principle, 50% of tokens are concentrated in the hands of developers, and there may be problems with regulators. NEO platform has already implemented a large number of scaling solutions, but is still developing sidechains and interoperability solutions.
Quantum is a promising blockchain with a powerful team. On September 13, 2017 a working network was launched. Since the network is new, some problems and vulnerabilities are identified in the process, which are quickly eliminated by the team. Interest in the project in the Internet has not subsided since it appeared. There are many topics for discussion in the context: ICO's record-breaking results, a prestigious team and investors, several test networks, large partners, etc. After successful test networks releases, the headlines about the “new Ethereum” appeared.
Ethereum has problems with speed and scalability, but it still holds a leading position among blockchains with smart contracts. Reputation outweighs all technical flaws. EOS, of course, has a number of significant advantages over Ethereum, however, until this blockchain launches, it’s too early to talk about competition.
And, considering the fact that between Dan Larimer and Vitalik Buterin there is a constant controversy over whose blockchain is better, EOS and Ethereum are the main competitors for each other.
Daniel Larimer's reply to Vitalik Buterin on criticism of EOS
Answer to Vitalik's Written Comments
- "Competitors" evaluation: 5 points out of 10. The outlook is neutral.
Direct competitors — 2 points out of 4 (high competition, including from already working projects).
Industry competitors — 2 points out of 4 (high competition).
Project monitoring of competition — 1 point out of 2 (it is missing in the project documentation, but Dan Larimer regularly speaks about his competitors).
The outlook is neutral. Despite the high competition, EOS has a number of competitive advantages: high speed and scalability, rich functionality, proven technology at the core, however, before a full launch of the platform, it is difficult to assess the performance and completeness of all these advantages.
Citation, social networks
In July-September 2017, a high promotion activity was observed: the project was presented at 7 summits and conferences in the US, England and Japan. In collaboration with FinTech Worldwide, EOS team conducted a series of 4 conferences throughout Europe and the US, starting at London Fintech Week 2017 on July 10-14.
Even when the platform was at development stage, it was already supported by thousands of people from all over the world. Meetups are held regularly, there is a high activity in telegram channel dedicated to the project (with more than 63 thousand participants), groups are being developed on Facebook, Twitter and Steemit. EOS is already widely known in crypto community and the project’s popularity only grows with time.
EOS also attracted the attention of crypto community because it is currently the project with the largest ICO in terms of attracted funds ($4.1 billion).
EOS popularity statistics in social networks:
- Reddit — 54.4 thousand subscribers,
- Twitter — 179 thousand subscribers,
- Facebook — 14.5 thousand subscribers,
- Telegram — 63 thousand participants.
Applicability/usability
According to etherscan, the released 1 billion of EOS tokens are distributed among over 330 thousand addresses.
The main network was launched only on June 2, 2018, and the project has already reached the TOP-5 by the number of daily transactions. The record is a little less than 1 million per day, the average value is 189.888 transactions per day (according to blocktivity.info).
During operation, the load on the platform has not yet reached the limits of its performance, the maximum speed that has been fixed is 592 TPS.
According to eosmonitor.io, more than 263 thousand accounts are registered in the network.
Projects on EOS technology
There are many decentralized applications (dApps) that are ready to be launched after the release of the main EOS network. Many of these dApps will distribute their tokens via airdrops between EOS token holders. These applications will be the first testers of EOS blockchain.
The following is an infographics of decentralized EOS applications ecosystem that are ready for the launch. It is worth noting that even more applications are under development.

- AZARUS — a platform for games and betting using tokens. Specially designed for video game industry.
- Billionaire Token — a decentralized blockchain-based games such as dice and cards. The tokens are deflationary, which means that the coins will be burned every week.
- Cards & Tokens — a platform for collectible digital cards, through which users can upload their content and earn money.
- Carmel — a decentralized open source educational platform for software developers. Tokens are used to develop a set of user skills.
- Chaince — a blockchain-asset trading platform that stimulates the development of EOS projects.
- Chintai — a global decentralized leasing platform for EOS tokens. Allows EOS token holders to get rewards by providing tokens to developers of decentralized applications.
- DEOS Games -— a gaming platform, a casino with zero profitability of the organizers.
- emanate — a musical and technological platform for cooperation and interaction between artists. Thanks to smart contracts, emanate allows artists to monetize the fruits of cooperation.
- EOS Bet — a gambling system in which investors can receive dividends.
- EOXCommerce — a decentralized e-commerce platform that allows to use cryptocurrency and crypto assets based on EOS as a means of payment.
- EOSfinex — a decentralized exchange created by Bitfinex.
- EOS Gems — a game based on EOS blockchain.
- Everipedia — an encyclopedia of the new generation (in fact, the fork of Wikipedia).
- HorusPay — a decentralized global portal that allows companies to share private, encrypted information with international suppliers.
- HireVibes — a single labor exchange where employers can post vacancies for free, hire candidates, communicate, pay for services.
- Insights Network — a blockchain-based data exchange where users can monetize information.
- IRYO — a decentralized medical data platform whereby patients completely control information, manage access rights, etc.
- Lab Ledger — a social network, crowdfunding site for scientists.
- Onepay — a payment system (POS) that allows companies to accept leading cryptocurrencies as a means of payment.
- ONO — a decentralized open source social network that allows content creators to get rewards.
- Parsec Frontiers — a massively multiplayer online game. The players themselves develop, improve and fully control the game.
- Plactal — a decentralized advertising platform focused on mobile gaming.
- Scatter — a wallet for storing identity data and keys. The blockchain base of the project is an identification layer to ensure trust in applications and users.
- Sense — a decentralized information market.
- SFEOS — a free, turn-based massively multiplayer online game with a presence effect (the subject is science fiction), built on EOS blockchain.
- Starteos — a smart wallet with EOS support.
- Tokena — a decentralized exchange based on EOS.
- Trade Stuff — a decentralized barter ecosystem built on EOS blockchain.
- TXT — a decentralized advertising platform that pays for views. Designed to encourage people to view ads.
- Uncloak — the world's first blockchain-based cybersecurity regulatory solution.
- Zimbra X — the next generation of Zimbra email platform.
Famous persons in the team
EOS team is led by blockchain veterans: Brendan Blumer, Dan Larimer, Brock Pierce, Ian Grigg. More details about each and about their contribution to the development of blockchain technologies can be found in “Team” subsection.
- "Fame of the project" evaluation: 9 points out of 10. The outlook is positive.
Citation, social networks — 3 points out of 3.
Usability / applicability — 2 points out of 2.
Projects based on technology — 2 points out of 3 (many little-known projects and startups).
Famous persons in the team — 2 points out of 2.
The outlook is positive. The project is known all over the world, despite the fact that the main network has been launched not long ago, it is already very actively used. The team is led by people who are world famous in the field of blockchain technologies and who have made a significant contribution to its development.
RATING. “EOS” evaluation: 58 points out of 70 — 82.86%. The outlook is neutral.
The outlook is neutral. A promising and actively developing project with an experienced team and proven technology. The success of the project as such and the investment attractiveness of the token directly depends on the success of implementation and distribution of projects based on EOS.io.
Factors in favor of the high prospects of this platform:
- Dan Larimer, the creator of the platform — is a real veteran of cryptographic industry. He has several successful projects, whose investors have repeatedly increased their investments. EOS is able to surpass these results, becoming a new word in the world of digital money.
- The stated rich and convenient functionality, high speed and scalability give the project a good competitive advantage
- 10% of tokens sent to the project team are distributed over a ten-year period. Such decision will encourage them to actively develop the platform.
- Consensus building algorithm used in the system greatly increases the speed of transactions and reduces transaction fees.
- The scale of the project attracts more and more new investors. During the ICO, enormous money was collected: in just the first 5 days of the ICO, a record for the entire industry — $170 million was collected. Part of the investment is spent on promotion and advertising, which attracts the attention of other potential investors.
- EOS has a powerful support represented by Steem. In fact, this is a platform for the widest advertising and an inexhaustible source of developers and investors. Having practically your own small media is already part of future success. Powerful information support can be considered guaranteed.
- EOS is built on the well-known and proven Graphene technology, on which BitShares, Steem and Golos were previously built.
However, there are certain risks. These include the following points:
- The creators of EOS have not yet demonstrated a working version of the platform, which means it is impossible to say with certainty whether it will support millions of users.
- All money raised during the ICO is used at the discretion of the project team, reporting to investors is formal.
- A number of similar platforms are being developed simultaneously with the platform. In addition, Ethereum itself, unwilling to give up the position, can easily switch to a more modern and fast version of the system.
- Rate instability. Constant changes in the token price obstruct its long-term outlook.
- The management of EOS is concentrated in the hands of a small circle of people. And the principle of delegation of transaction processing (DPoS algorithm) is considered by many as a centralized system that violates the basic principles of cryptocurrency — decentralization and independence.
- Paradoxically, the participation of Dan Larimer both helps and harms the project. This is due to the fact that in the crypto community, Larimer has a reputation of a person who does not complete what he has begun. However, this does not mean that Dan’s possible leaving will stop the work on the project.
Nevertheless, the above disadvantages can be equally attributed to almost all platforms launched today. And investors continue to invest in the platform, despite the risks.
Also members of crypto community express concerns about DPoS consensus building algorithm, which is that this approach opens up opportunities for dishonest players. These concerns are supported by the words of cryptocurrency analyst Tone Vays, who acted as a consultant in previous projects of Larimer: “Dan Larimer launched several projects based on PoS, and they were rather dubious in nature. Both BitShares and Steemit allowed insiders to create a large number of tokens for themselves, and after that, proof-of-stake algorithm allowed them to stamp those valuable tokens without limitations”. However, the algorithm is constantly tested in work conditions and is being finalized, which can be seen on the example of BitShares, where its operation principles have changed several times over the past six months, eliminating the disadvantages that arise and improving the operation of the algorithm.
References
- Official website: https://eos.io/
- GitHub: http://github.com/eosio
- Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/eosblockchain
- Twitter: http://twitter.com/eos_io
- Telegram: https://eos.io/chat/
- Developer site: http://www.block.one/
Russian thread on Bitcointalk: https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?topic=1899734.0
- “Fame” section was added as an additional parameter for project evaluation. The weight of the section in the rating system is 10 points.
- The content of “Project Fame” subsection has been moved from “Statistics” section to “Fame” section.
- In connection with changes indicated in par.2, there was made a redistribution of points of “Statistics” section evaluation, the overall evaluation did not change.
In connection with the above changes, the overall rating of the project has changed from 49 points out of 60 — 81.67% to 58 points out of 70 — 82.86%.